NEWS RELEASES
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
January 17, 2007
Sandia computer simulation monitors traffic in contraband nuclear material
Unique procedure arouses United Nations interest
Download 300dpi JPEG image, “nuclear-tracking.jpg,” 700 KB (Media are welcome to download/publish this image with related news stories.)
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A Sandia National Laboratories researcher has developed a simulation program designed to track the illicit trade in fissile and nonfissile radiological material well enough to predict who is building the next nuclear weapon and where they are doing it.
“By using a cluster analysis algorithm coded into a program,” says Sandia researcher David York. “I evaluated those traffic patterns and routes in which thefts, seizures, and destinations of materials were reported. Data from these examinations were enough to allow me to retrospectively depict the A. Q. Kahn network before it was uncovered.”
Kahn is a Pakistani scientist linked to the illicit proliferation of nuclear technical knowledge. Cluster analyses link data of common place, time, or material. Testing a computer simulation on a known past event is one accepted means of establishing the program’s validity.
Sandia is a National Nuclear Security Administration laboratory.
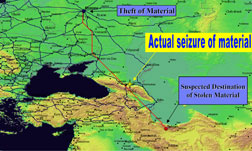 THIS SLIDE REPRESENTS a pathway analysis where the red line is computed via a cluster analysis of specific weighting factors. These factors are deduced from available intelligence to the analyst conducting the trafficking analysis. The actual seizure site of this particular incident was in Grozny, Chechnya, depicted by the yellow star. Based on available intelligence, it is apparent that the pathway analysis follows a probabilistic route taken by the traffickers.
THIS SLIDE REPRESENTS a pathway analysis where the red line is computed via a cluster analysis of specific weighting factors. These factors are deduced from available intelligence to the analyst conducting the trafficking analysis. The actual seizure site of this particular incident was in Grozny, Chechnya, depicted by the yellow star. Based on available intelligence, it is apparent that the pathway analysis follows a probabilistic route taken by the traffickers.Download 300dpi JPEG image, “fissile.jpg,” 412 KB (Media are welcome to download/publish this image with related news stories.)
In the Kahn analysis, York generated an analysis of networked routes indicative of a nuclear trafficking scheme between countries. In several verified incidents, inspectors seized uranium enriched to 80 percent, as well as dual-use items indicative of small-scale development of crude nuclear devices.
In the study, York collected and collated data from 800 open-source incidents from 1992 to the present, along with the movement of dual-use items like beryllium and zirconium. He plotted the incidents on a geographic information system (GIS) software platform. He came up with a network of countries and routes between countries indicative of an illicit nuclear and radiological trafficking scheme.
“The number of incidents and the quantity and quality of material seized is disturbing,” York says, “particularly because this may represent a small percentage of the actual amount of material being trafficked.”
The situation may be worse than it appears because much information about nuclear material traffic is classified, York says, to prevent embarrassment to countries through which a nuclear weapon or the materials to fabricate a weapon may have passed.
York presented his results in October at the International Safeguards Conference sponsored by the United Nation’s International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in Vienna, Austria. He has also been invited to present his methods and conclusions to the European Union’s Illicit Trafficking Working Group at the June meeting of the IAEA.
How does the method work? “One begins by conducting cluster analyses on the GIS platform for material or activity similar to the incident in question. This gives the analyst an idea of corridors used by potential smugglers. It also indicates where the material might have come from and where it is,” says York. “If the trafficker has only a certain amount of time to reach a destination and you have that information, one can ask what is the shortest route from point A to point B, or find major highways needed to accommodate a large shipment.”
For the tool to be effective, “Enough information must be collected under a cooperative international framework,” York says. “Then info must be analyzed to separate patterns from noise, essentially creating intelligence.”
Nation-states that reuse nuclear fuel through reprocessing can create and ship dangerous materials that previously were confined to the more industrialized world.
“We’re trying to develop a market niche for this kind of tracking program,” says Sandia manager Gary Rochau, “and I think we’re ahead of everyone’s headlights.”
The method can be used to track other materials, such as drugs. “We have a lot of interest from a lot of agencies,” says Rochau.
Trafficking may be engaged in by amateur smugglers trying to feed their families in a post-Soviet era. It may also be practiced by those involved in organized crime who find a lucrative market in moving illicit materials, and by terrorists interested in the potential devastation and psychological effects of the use of nuclear materials.
York developed the program as part of his master’s thesis while a student intern at Sandia.
Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin company, for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration. Sandia has major R&D responsibilities in national security, energy and environmental technologies, and economic competitiveness.
Sandia news media contact: Neal Singer, nsinger@sandia.gov, (505) 845-7078